The use of sea sand and chloride ion standards will be standardized. Admixtures and additives must be tested
A few days ago, the Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of Guangdong Province publicly solicited opinions on the Guangdong Provincial Standard "Concrete Chloride Ion Quality Control Standards". The province's sea sand use and chloride ion standards will be standardized.
It is understood that the "standard" puts forward chloride ion control requirements for concrete production raw materials, mixtures, and hardened concrete, and admixtures, admixtures, and mixing water are also included in the chloride ion control range.
The "Standard" requires that every batch of sand must be tested for chloride ion content when entering the site; sea sand should not be used for construction sand, and it is strictly forbidden to use sea sand that has not been desalinated; sea sand must not be used for prestressed concrete.
At the same time, the "Standard" also stipulates the testing frequency, rules, etc., and proposes detailed testing methods.
Regulations on the Control of Chloride Ion Content in Raw Materials
cement
The chloride ion content in cement should not exceed 0.10%.
Construction sand
The chloride ion content of reinforced concrete sand shall not exceed 0.03%, and the chloride ion content of prestressed concrete sand shall not exceed 0.02%.
Building stones
For concrete stones that have the risk of chloride salt corrosion and are not stored in a closed storage, they should be controlled with reference to the technical requirements and test methods of the chloride ion content in the sand.
Admixture
The content of chloride ion in admixtures such as fly ash, granulated blast furnace slag powder, silica fume, etc. should not exceed 0.06%.
Admixture
The chloride ion content in the admixture should not exceed 0.6%.
Water for mixing
For reinforced concrete structures, the chloride ion content in the mixing water shall not exceed 1000mg/L; for prestressed concrete structures, the chloride ion content in the mixing water shall not exceed 500mg/L. For structural concrete with a design service life of 100 years, the chloride ion content in the mixing water shall not exceed 500 mg/L.
Regulations on the Control of Chloride Ion Content in Concrete Mixtures
For concrete structures with a design service life of 50 years, the maximum content of water-soluble chloride ions in the concrete mixture should meet the following requirements:
For concrete structures with a design service life of 100 years, the maximum chloride ion content in hardened concrete shall not exceed 0.06%.
testing regulations
Inspection of chloride ion content in raw materials
1 When raw materials enter the site, the raw material supplier shall provide the quality certificate of the batch of materials, factory inspection report, type inspection and other quality certification documents, and special materials shall also have instructions for use.
2 The chlorine ion content of the raw material on-site inspection certificate or factory inspection report shall be indicated, and the chloride ion content control for the on-site inspection shall meet the following requirements:
Each batch of construction sand shall be inspected for chloride ion content;
The stones affected by the corrosion of chloride salt shall be tested for chloride ion content in each batch according to the technical requirements of sand chloride ion content;
When the cementitious material is used for the first time, the chloride ion content should be checked. Cementing materials such as cement, fly ash and slag powder of the same manufacturer, same brand and same type shall be inspected for chloride ion content no less than once a year;
When the admixture is used for the first time, a chloride ion content inspection should be carried out. For admixtures of the same manufacturer and type, no less than one chloride ion content inspection shall be carried out every quarter;
The inspection of the chloride ion content of the mixing water should meet the requirements of the "Water Standard for Concrete" JGJ63, and the inspection requirements of tap water are not required;
Inspection of chloride ion content in concrete mixture
1 The chloride ion inspection of concrete mixture is divided into factory inspection and delivery inspection. The sampling and testing work for the delivery inspection is carried out by the concrete supplier, and the sampling and testing work for the delivery inspection is carried out by the concrete buyer.
2 Before leaving the factory for the concrete with the same sand source, the supplier shall conduct at least one water-soluble chloride ion inspection of the mixture.
3 The delivery inspection of water-soluble chloride ion content in the concrete mixture of the same project and the same mix ratio shall not be less than once, and the third-party inspection agency shall be responsible for the inspection; when the concrete raw materials change, the concrete mixture shall be re-tested The content of water-soluble chloride ions is tested.
4 The concrete production enterprise shall entrust a third-party inspection agency to conduct not less than one mix chloride ion inspection on the same mix concrete every year.
5 During the construction process, according to the needs of project quality control, random samples can be taken at the pouring site for chloride ion inspection of the concrete mixture.
6 If the chloride ion of the concrete mixture fails the factory inspection, it shall not leave the factory. If the delivery inspection fails, the concrete shall be returned.
Inspection of chloride ion content in hardened concrete
1 The concrete shall be tested for the chloride ion content of hardened concrete. When there are special requirements for key projects or designs, the acid solution method should be adopted, which shall meet the requirements of this standard.
2 For the same project and the same strength grade concrete, the number of chloride ion content detections in hardened concrete should be no less than one group.
3 The chloride ion detection of hardened concrete shall be carried out by a qualified third-party inspection agency.
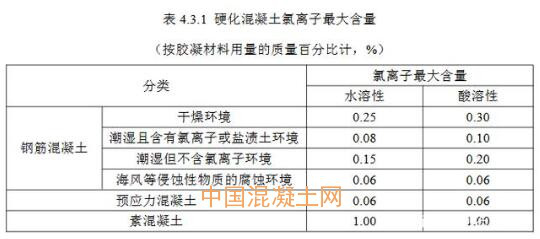
4 When the chloride ion content of hardened concrete meets the requirements of Table 4.3.1, it is judged as qualified. When unqualified, double sampling of the same batch of solid concrete shall be re-inspected according to the acid solution method. If all the re-inspection results are qualified, it will be deemed qualified. If the re-inspection results are still unqualified, it will be deemed unqualified.
5 When the theoretical calculation value of the concrete chloride ion content calculated according to the mix ratio of the concrete chloride ion content or the detection of the chloride ion content of the mixture is unqualified, and has been applied to engineering concrete, the batch of hardened concrete and two adjacent batches of hardened concrete should be chlorinated. Ion detection. The final result of the chloride ion test of hardened concrete shall prevail.
6 When there is a dispute about the chloride ion content of hardened concrete, the acid-soluble chloride ion content shall be used as the final result for evaluation.
7 When the chloride ion content in the hardened concrete is unqualified, the construction unit and the concrete production unit shall submit a summary analysis report and a quality accident plan, and after passing expert evaluation and evaluation, a follow-up special treatment technical plan shall be formulated and implemented after design review.